# Git Branching Model
# Main branches
At the core, the development model is greatly inspired by existing models out there. The central repo holds two main branches with an infinite lifetime:
- master
- develop
# Key concept
- Parallel to the master branch, another branch exists called develop.
- consider origin/master to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects a production-ready state.
- We consider origin/develop to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects a state with the latest delivered development changes for the next release. Some would call this the “integration branch”. This is where any automatic nightly builds are built from.
- When the source code in the develop branch reaches a stable point and is ready to be released, all of the changes should be merged back into master somehow and then tagged with a release number. How this is done in detail will be discussed further on.
- Therefore, each time when changes are merged back into master, this is a new production release by definition. We tend to be very strict at this, so that theoretically, we could use a Git hook script to automatically build and roll-out our software to our production servers everytime there was a commit on master.
# Supporting branches
Next to the main branches master and develop, our development model uses a variety of supporting branches to aid parallel development between team members, ease tracking of features, prepare for production releases and to assist in quickly fixing live production problems. Unlike the main branches, these branches always have a limited life time, since they will be removed eventually.
- Feature branches
- Release branches
- HotFix branches
# Key concept
- Each of these branches have a specific purpose and are bound to strict rules as to which branches may be their originating branch and which branches must be their merge targets.
# Feature branches
- Feature branches (or sometimes called topic branches) are used to develop new features for the upcoming or a distant future release. When starting development of a feature, the target release in which this feature will be incorporated may well be unknown at that point. The essence of a feature branch is that it exists as long as the feature is in development, but will eventually be merged back into develop (to definitely add the new feature to the upcoming release) or discarded (in case of a disappointing experiment).
- Feature branches typically exist in developer repos only, not in origin.
# Creating a feature branch
$ git checkout -b myfeature develop
# Switched to a new branch "myfeature"
# Incorporating a finished feature on develop
$ git checkout develop
# Switched to branch 'develop'
$ git merge --no-ff myfeature
# Updating ea1b82a..05e9557
#(Summary of changes)
$ git branch -d myfeature
# Deleted branch myfeature (was 05e9557).
$ git push origin develop
--no-ffflag causes the merge to always create a new commit object, even if the merge could be performed with a fast-forward. This avoids losing information about the historical existence of a feature branch and groups together all commits that together added the feature
# Release branches
- Release branches support preparation of a new production release. They allow for last-minute dotting of i’s and crossing t’s. Furthermore, they allow for minor bug fixes and preparing meta-data for a release (version number, build dates, etc.).
- The key moment to branch off a new release branch from develop is when develop (almost) reflects the desired state of the new release.
# Creating a release branch
# Release branches are created from the develop branch. For example, say version 1.1.5 is the current production release and we have a big release coming
# up. The state of develop is ready for the “next release” and we have decided that this will become version 1.2 (rather than 1.1.6 or 2.0). So we branch
# off and give the release branch a name reflecting the new version number:
$ git checkout -b release-1.2 develop
# Switched to a new branch "release-1.2"
$ ./bump-version.sh 1.2
# Files modified successfully, version bumped to 1.2.
$ git commit -a -m "Bumped version number to 1.2"
# [release-1.2 74d9424] Bumped version number to 1.2
# 1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
- After creating a new branch and switching to it, we bump the version number. Here, bump-version.sh is a fictional shell script that changes some files in the working copy to reflect the new version. (This can of course be a manual change—the point being that some files change.) Then, the bumped version number is committed.
- This new branch may exist there for a while, until the release may be rolled out definitely. During that time, bug fixes may be applied in this branch (rather than on the develop branch). Adding large new features here is strictly prohibited. They must be merged into develop, and therefore, wait for the next big release.
# Finishing a release branch
# When the state of the release branch is ready to become a real release, some actions
# need to be carried out. First, the release branch is merged into
# master (since every commit on master is a new release by definition, remember). Next,
# that commit on master must be tagged for easy future reference to
# this historical version. Finally, the changes made on the release branch need to be
# merged back into develop, so that future releases also contain these
# bug fixes.
$ git checkout master
# Switched to branch 'master'
$ git merge --no-ff release-1.2
# Merge made by recursive.
# (Summary of changes)
$ git tag -a 1.2
# To keep the changes made in the release branch, we need to merge those back into
# develop, though. In Git:
$ git checkout develop
# Switched to branch 'develop'
$ git merge --no-ff release-1.2
# Merge made by recursive.
# (Summary of changes)
# This step may well lead to a merge conflict (probably even, since we have changed
# the version number). If so, fix it and commit.
# Now we are really done and the release branch may be removed, since we don’t need it
# anymore:
$ git branch -d release-1.2
# Deleted branch release-1.2 (was ff452fe).
# Hotfix branches
- Hotfix branches are very much like release branches in that they are also meant to prepare for a new production release, albeit unplanned. They arise from the necessity to act immediately upon an undesired state of a live production version. When a critical bug in a production version must be resolved immediately, a hotfix branch may be branched off from the corresponding tag on the master branch that marks the production version.
- The essence is that work of team members (on the develop branch) can continue, while another person is preparing a quick production fix.
# Creating the hotfix branch
# Hotfix branches are created from the master branch. For example, say version 1.2 is
# the current production release running live and causing troubles due to a severe bug.
# But changes on develop are yet unstable. We may then branch off a hotfix branch and
# start fixing the problem:
$ git checkout -b hotfix-1.2.1 master
# Switched to a new branch "hotfix-1.2.1"
$ ./bump-version.sh 1.2.1
# Files modified successfully, version bumped to 1.2.1.
$ git commit -a -m "Bumped version number to 1.2.1"
# [hotfix-1.2.1 41e61bb] Bumped version number to 1.2.1
# 1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
# Don’t forget to bump the version number after branching off!
# Then, fix the bug and commit the fix in one or more separate commits.
$ git commit -m "Fixed severe production problem"
# [hotfix-1.2.1 abbe5d6] Fixed severe production problem
# 5 files changed, 32 insertions(+), 17 deletions(-)
# Finishing a hotfix branch
# When finished, the bugfix needs to be merged back into master, but also needs to be
# merged back into develop, in order to safeguard that the bugfix is included in the
# next release as well. This is completely similar to how release branches are finished.
# First, update master and tag the release.
$ git checkout master
# Switched to branch 'master'
$ git merge --no-ff hotfix-1.2.1
# Merge made by recursive.
# (Summary of changes)
$ git tag -a 1.2.1
# Next, include the bugfix in develop, too:
$ git checkout develop
# Switched to branch 'develop'
$ git merge --no-ff hotfix-1.2.1
# Merge made by recursive.
# (Summary of changes)
- The one exception to the rule here is that, when a release branch currently exists, the hotfix changes need to be merged into that release branch, instead of develop. Back-merging the bugfix into the release branch will eventually result in the bugfix being merged into develop too, when the release branch is finished. (If work in develop immediately requires this bugfix and cannot wait for the release branch to be finished, you may safely merge the bugfix into develop now already as well.)
# Finally, remove the temporary branch:
$ git branch -d hotfix-1.2.1
# Deleted branch hotfix-1.2.1 (was abbe5d6).
# Summary
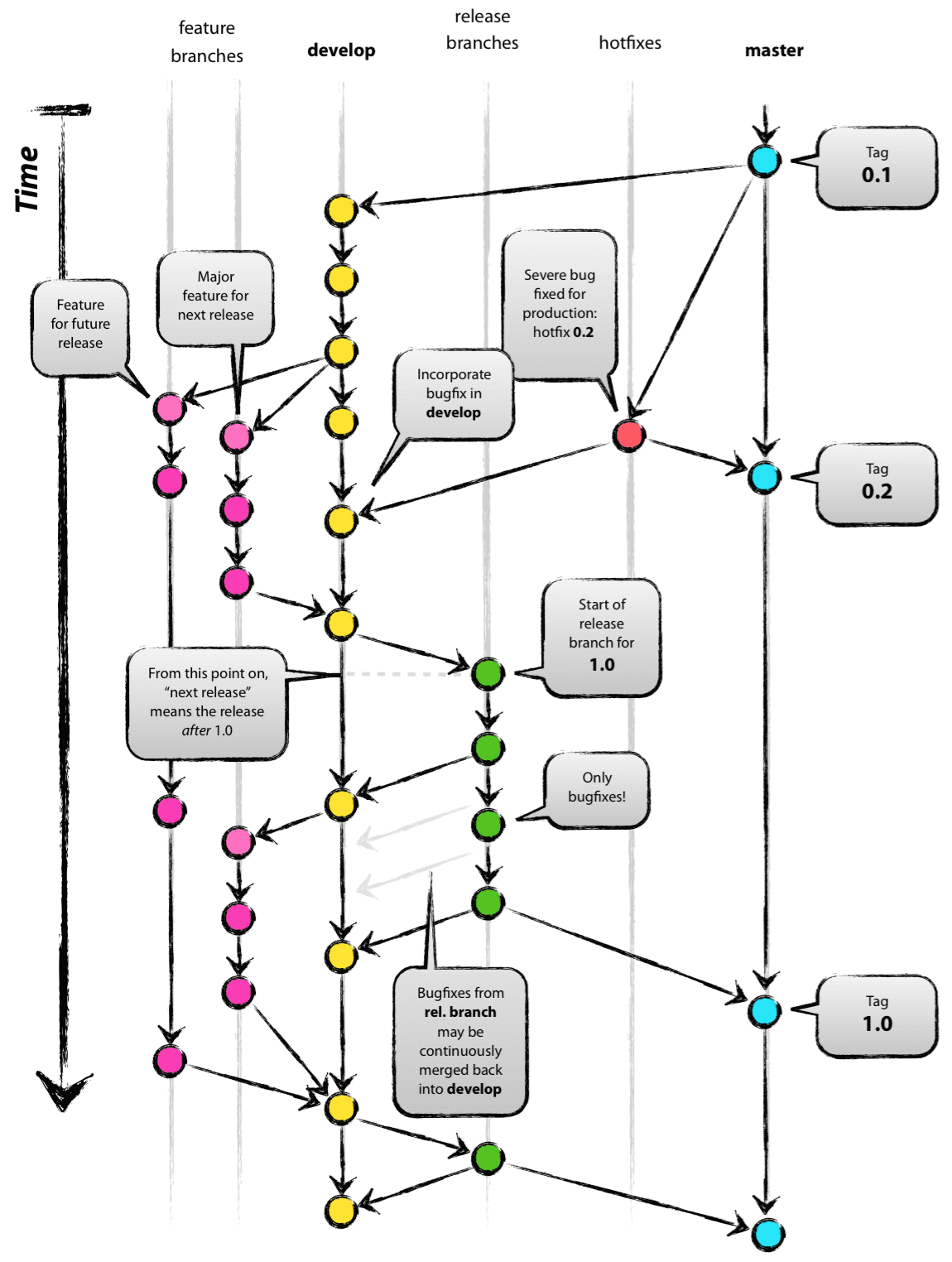
While there is nothing really shocking new to this branching model, the “big picture” figure that this post began with has turned out to be tremendously useful in our projects. It forms an elegant mental model that is easy to comprehend and allows team members to develop a shared understanding of the branching and releasing processes.